Smart Materials in Haptic Technology:
Can it be used as aids for the Visually Impaired?
The project focuses on exploring how currently available shape memory materials can be incorporated into haptic technology applications in order to improve the wellbeing and lifestyles of the blind and visually impaired.
Current haptic devices tend to be bulky, loud and produce unpleasant ‘mechanical’ feedback. Shape memory materials have the ability to be thin, light weight and flexible.
Demonstration
How can smart materials effectively provide haptic feedback?
Perception
How are these new types of haptic feedback perceived?
Usefulness
Is it useful for the visually impaired?
The Research
Shape Memory Materials
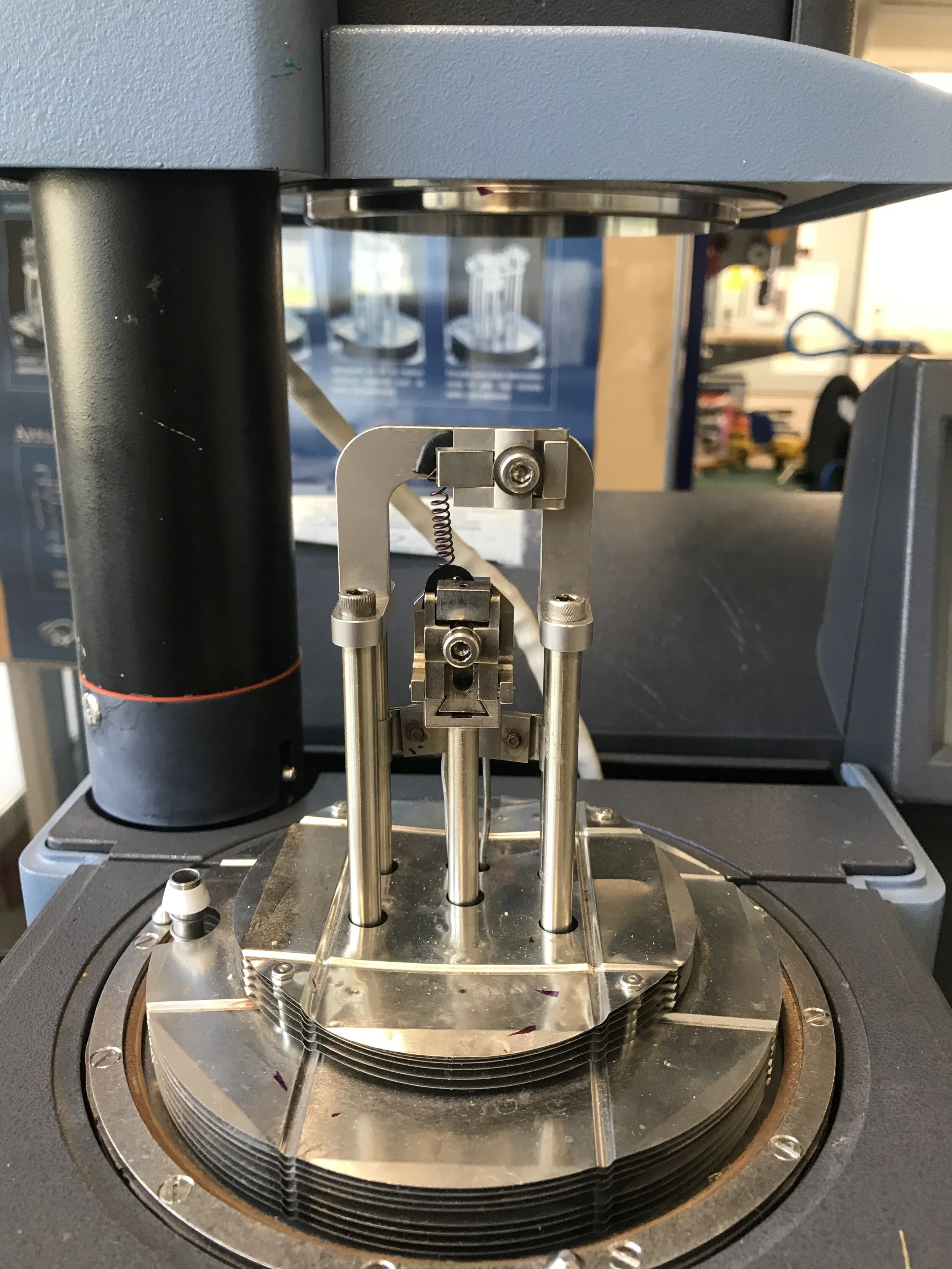
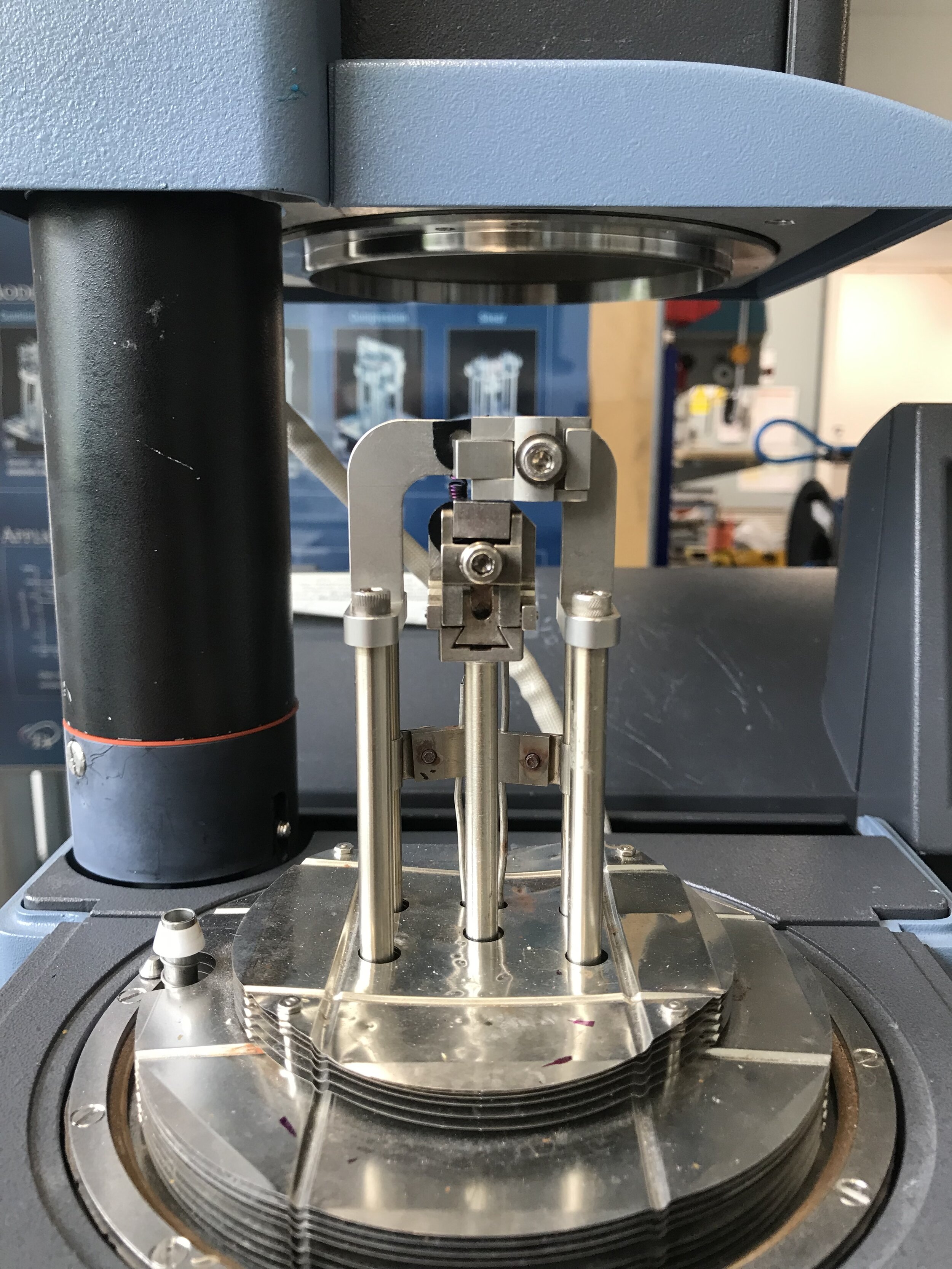
Shape memory materials are smart materials that have the ability to recover their original shapes from a deformation when a stimulus is applied to them. Both shape memory polymers and alloys were tested in different formats. Shape memory alloys were selected to move forward in this project, as they were easier to control and could be used in close proximity to skin.
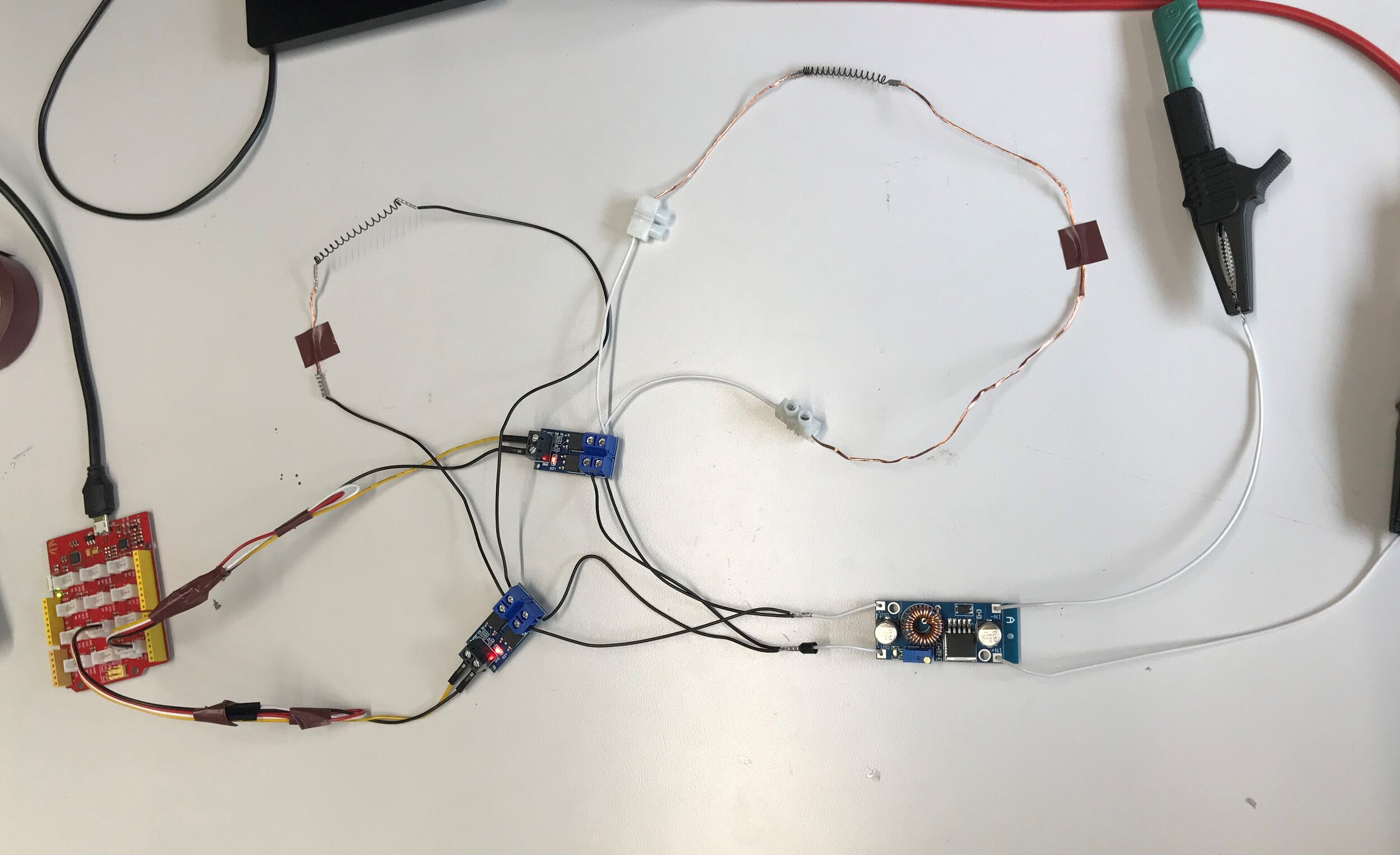
Exploring Actuators
Shape memory alloy wires were then incorporated into different formats of actuators in order to test their abilities of providing haptic feedback. Some of the formats can be found in the following videos.
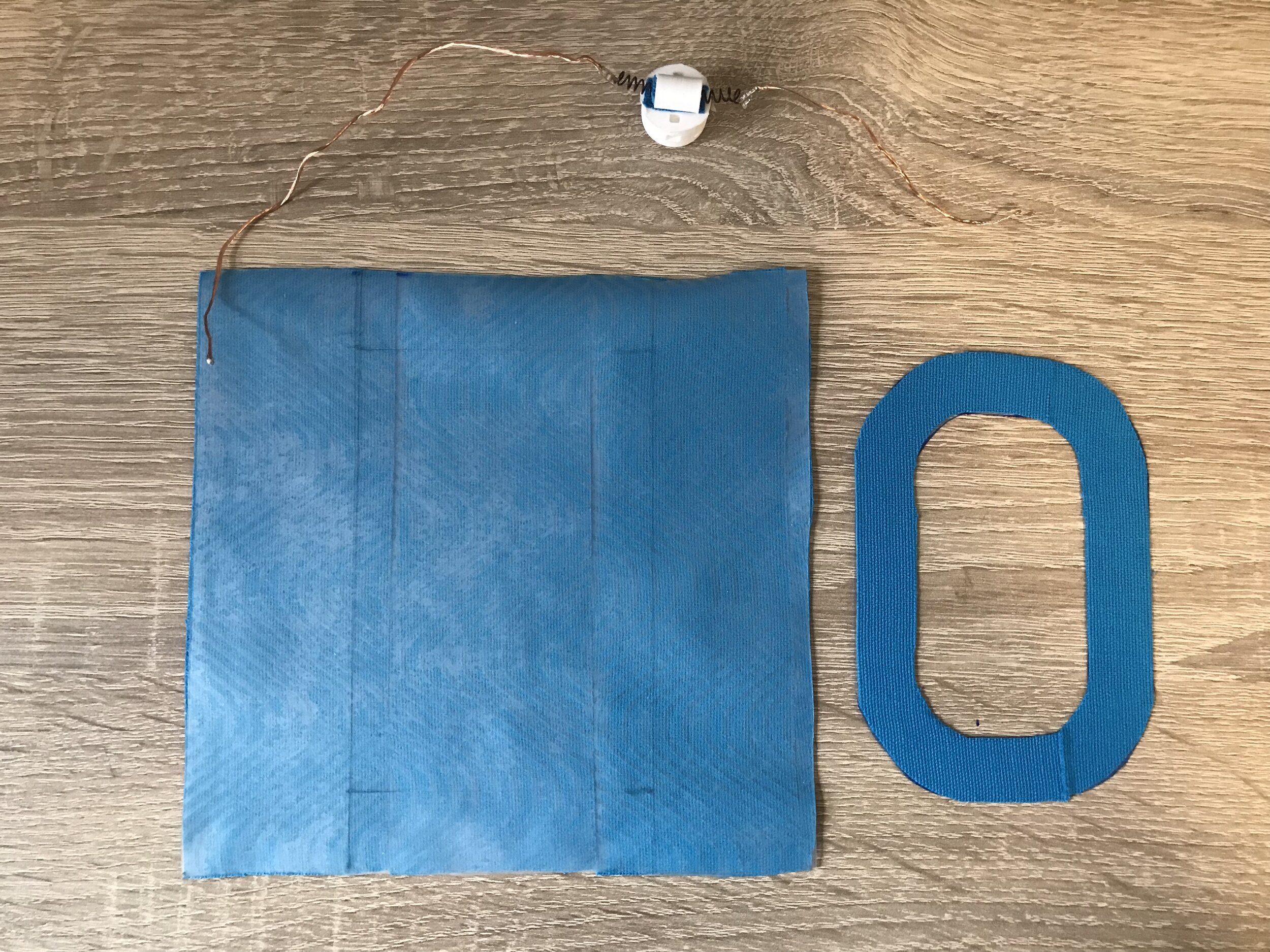
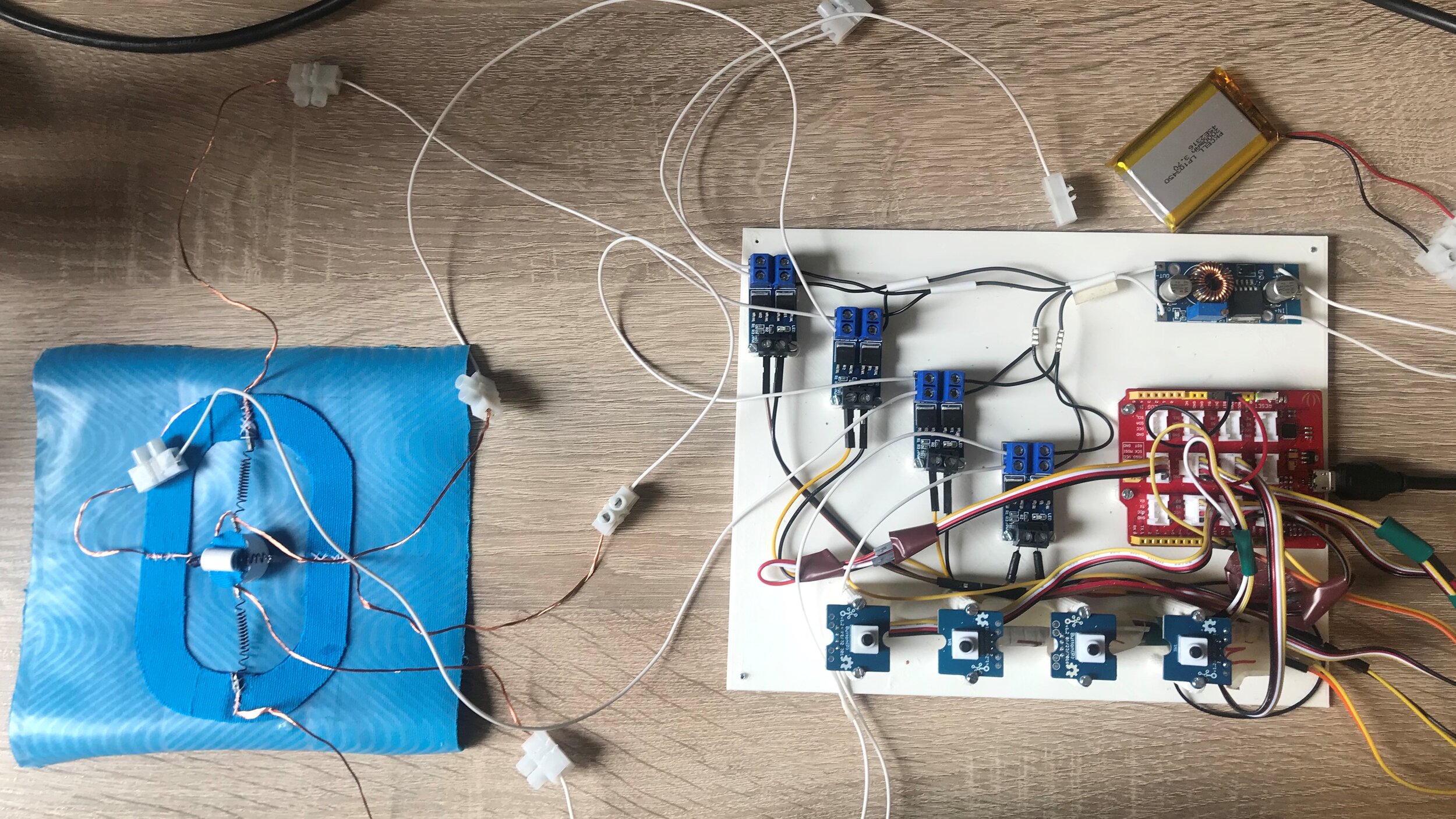
The Demonstrator
After exploring different types of actuators, it was decided that the demonstrator should be able to provide multiple types of feedback.
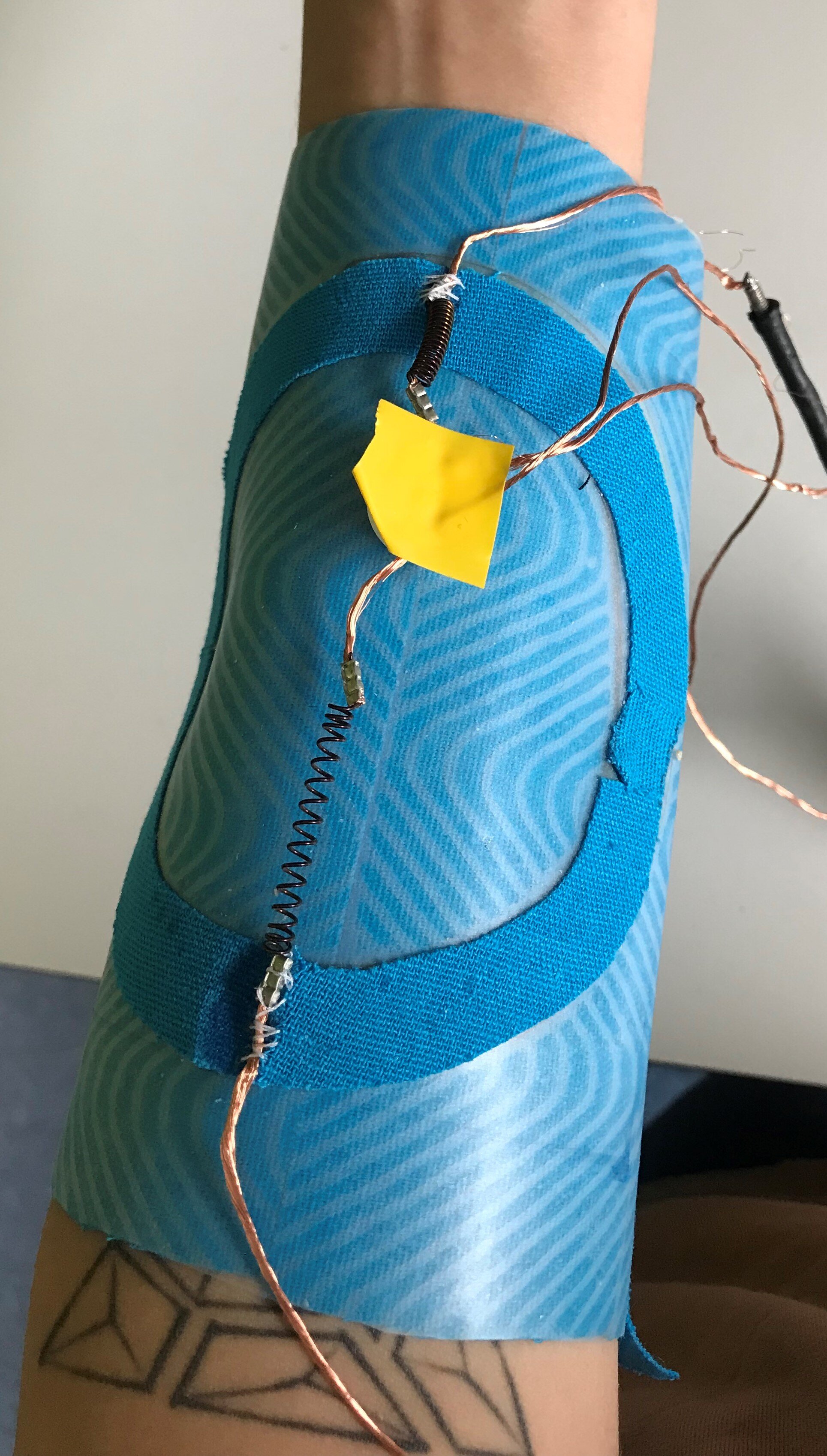
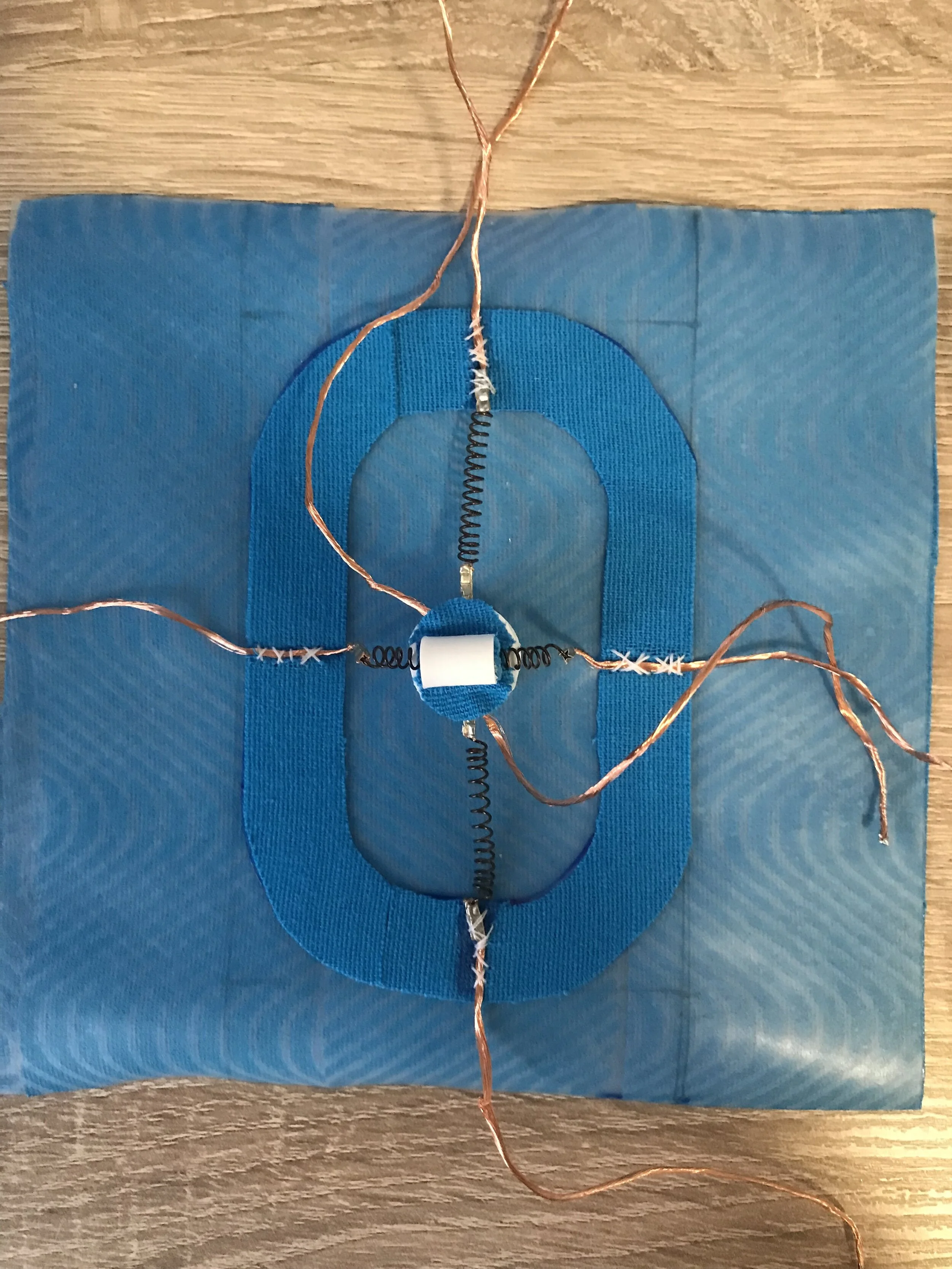
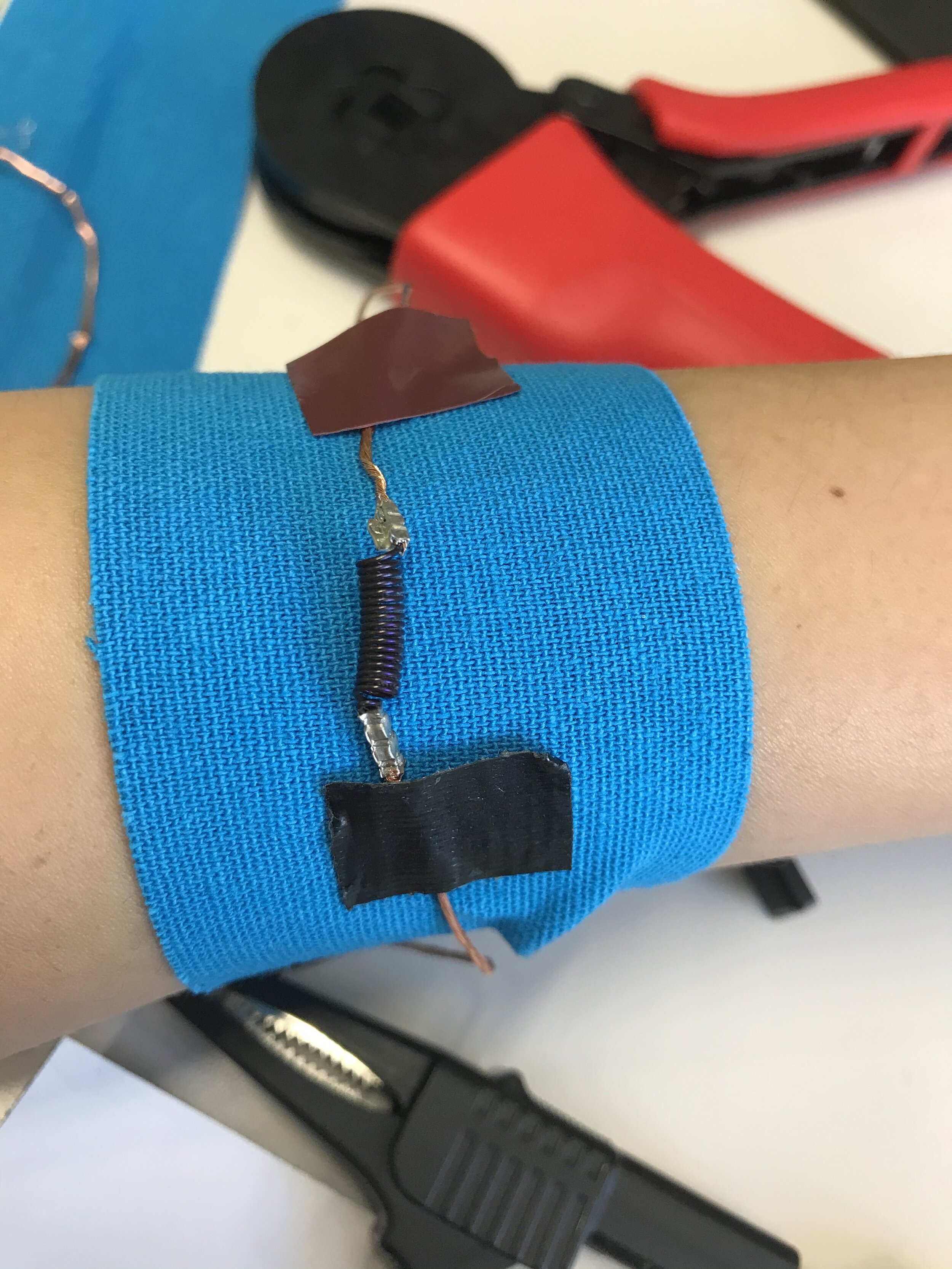
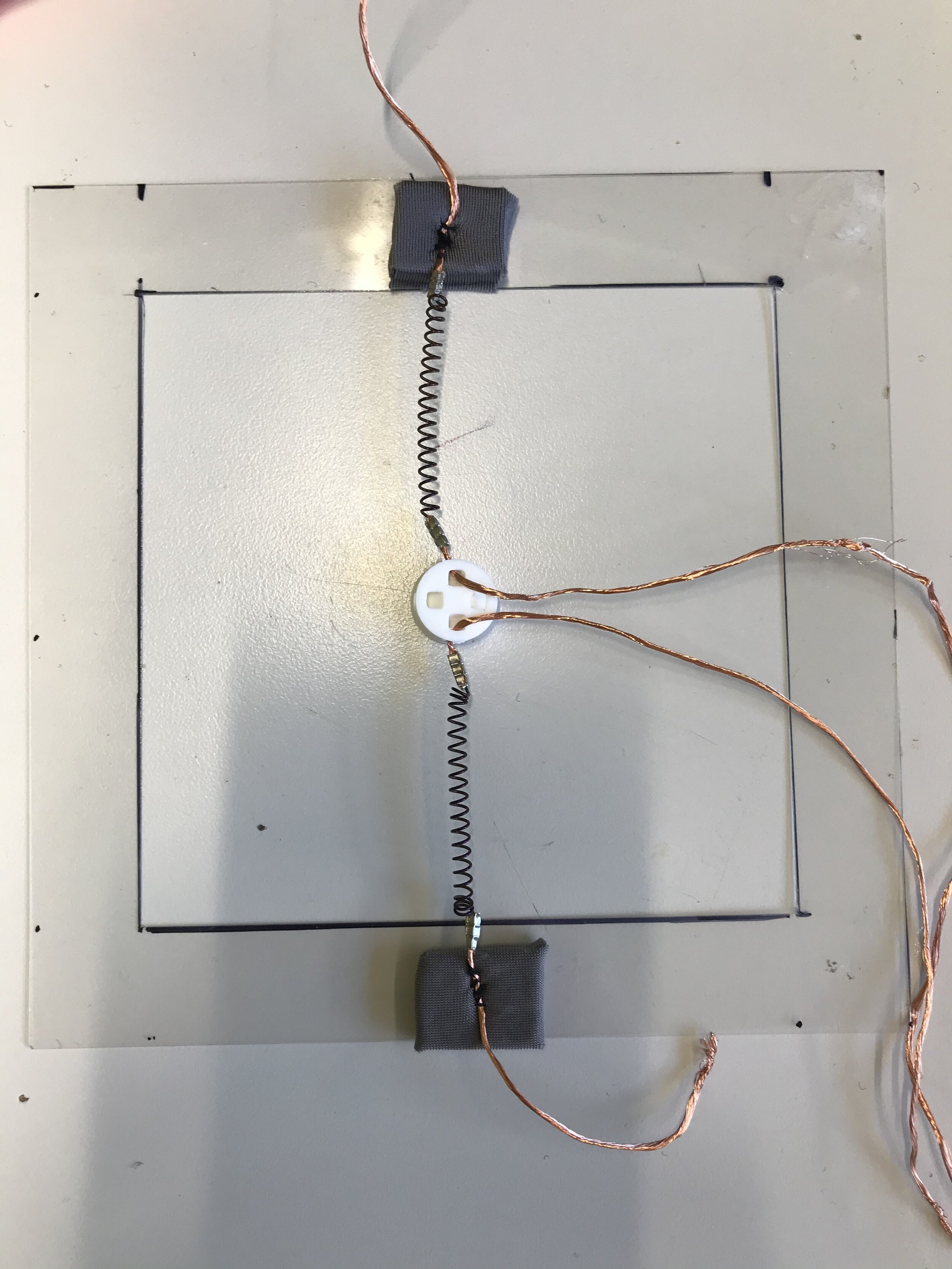
The final demonstrator consists of three shape memory alloys in the form of springs. It is capable of two different types of feedback- dragging (in two directions) and squeezing.
The Build
Testing with the Target Group
Testing was done with 4 participants having different types of visual impairment.
Purpose:
What sensations are perceived?
Are they distinguishable?
Could this type of feedback be useful?
Sensations:
“Organic and natural”
“Wheel moving along the arm”
“Finger on the skin”
“Massage”
“Non-directional pressure”
Distinguishable feedback
Recommendations
The technology is to be further worked upon to reduce the size of the electronics. It was recommended that the feedback and purpose of the future device be customizable to specific needs.
For example:
Navigation
Obstacle detection
Aids to crossing traffic
Remote care
Project Details
Graduation Thesis Project 2021 (individual)
Duration: 6 months
TU Delft (Netherlands)